This course equips participants with the essential skills to design, build, and customize Linux for modern embedded devices. Starting with the Embedded Linux ecosystem, participants learn how Linux fits into standard & custom hardware, the role of the bootloader, kernel, and root filesystem, and how these components come together to power embedded products.
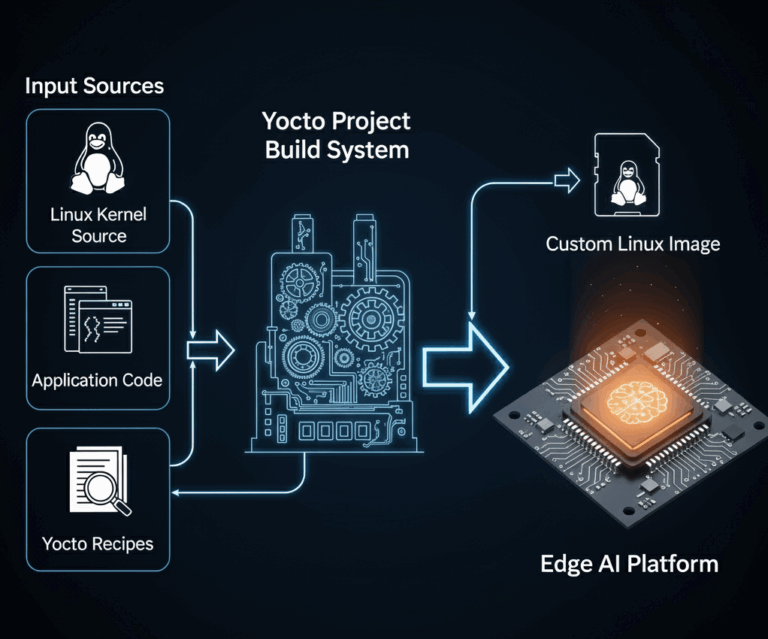
A major focus of the program is on Yocto Project, the industry-standard framework for creating custom Linux distributions. Participants explore how to use Yocto to build highly tailored systems — from configuring the kernel and selecting packages to creating board support packages (BSPs) and integrating custom applications.
Our Embedded Linux and Yocto training methodology is designed to ensure participants move beyond surface-level knowledge and gain deep, hands-on expertise. We follow a learn-by-doing approach, where every concept is tied directly to practical application. Instead of overwhelming learners with only theory, we break down each module into short conceptual sessions followed by immediate lab exercises. This helps participants not only understand how Linux and Yocto fit into the embedded ecosystem but also internalize why certain design decisions are made and how to troubleshoot real-world issues when systems behave unexpectedly.
The training emphasizes progressive complexity, starting from fundamental embedded Linux concepts, moving into board bring-up, cross-compilation, root filesystems, and kernel customization, and then advancing into Yocto-based build systems, recipes, and layers. Throughout the course, we use guided walkthroughs, real hardware demos, and structured labs so participants directly experience building, customizing, and debugging Linux systems for embedded targets
Aspiring participants must have the following skills before they wish to enroll for this program:
OR
Yes. These are industry-demanded skills, especially for roles such as Embedded Linux Engineer, Yocto Engineer, BSP Developer, and Embedded Systems Developer.
Embedded Linux gives you the foundation (boot process, kernel, device tree, rootfs), while Yocto teaches you how to build and customize complete Linux distributions for embedded devices. This course blends both, so you learn how they complement each other in real product development.
Without understanding core aspects of kernel, learning Embedded Linux remains superficial and procedural.
Proper grounding on core aspects of Linux programming and its fundamental concepts, will greatly enhance your ability to debug embedded Linux issues effectively and understand the overall development process better.
Our recommended boards for this program it:

Over 75 Onsite Trainings | 45+ Happy Clients | 10,000+ Careers Transformed Since 2003